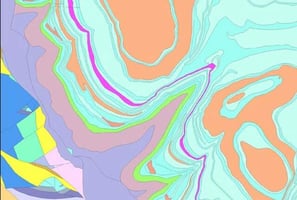
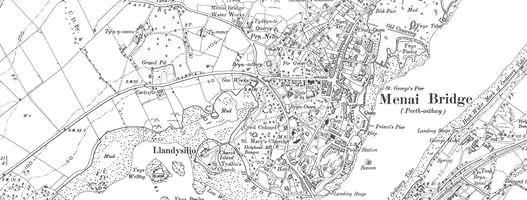
In the world of remote sensing and geospatial data collection, two technologies have emerged as...
LiDAR Data Unveiled: Enhancing Terrain Modeling and Analysis: Understanding the power of LiDAR data.
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology has revolutionised the way we perceive and analyse our environment. By emitting laser pulses and measuring their return time, LiDAR systems create highly accurate 3D representations of landscapes, buildings, and objects. In this blog, we delve into the power of LiDAR data, particularly its impact on terrain modelling and analysis.
 The Basics of LiDAR
The Basics of LiDAR
LiDAR works by emitting laser beams toward the ground or other surfaces. These lasers bounce back after hitting objects and the system measures the time it takes for the return signal to arrive. By combining these time-of-flight measurements with GPS data, LiDAR is able to generate highly precise 3D point clouds.
LiDAR offers several significant advantages for mapping and surveying applications. It provides high-resolution data, delivering detailed elevation and surface information that surpasses traditional methods like photogrammetry, making it ideal for applications such as topographic mapping, forestry analysis and urban planning. Unlike optical sensors, LiDAR performs effectively in a wide range of weather conditions, including fog, rain and low-light environments, ensuring consistent and reliable data collection. Additionally, LiDAR is non-intrusive, allowing large areas to be scanned quickly without physical contact or disruption to the environment, which is especially valuable for surveying difficult or hazardous terrain. Beyond these benefits, LiDAR can also penetrate vegetation to capture ground surfaces underneath tree canopies and when combined with GPS and inertial measurement systems, it produces highly accurate 3D point clouds that support advanced modelling, simulation and decision-making across industries.
Terrain Modelling with LiDAR
Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) derived from LiDAR provide highly accurate representations of terrain elevations. These models are invaluable for applications such as flood risk assessment, urban planning, and infrastructure design, offering detailed insights into the landscape. By capturing precise information about slope, aspect and landform characteristics, LiDAR-derived DEMs enable better decision-making in environmental management, construction planning and natural hazard mitigation. LiDAR data plays a crucial role in hydrological modelling by providing detailed elevation information that helps delineate watersheds, stream networks, and flow accumulation areas. Hydrologists use these LiDAR-derived datasets to simulate water flow patterns, predict flooding, and analyse drainage behaviour with high precision. The accuracy and resolution of LiDAR data allow for more reliable modelling of surface water dynamics, supporting effective water resource management, flood risk assessment, and environmental planning.
LiDAR data plays a crucial role in hydrological modelling by providing detailed elevation information that helps delineate watersheds, stream networks, and flow accumulation areas. Hydrologists use these LiDAR-derived datasets to simulate water flow patterns, predict flooding, and analyse drainage behaviour with high precision. The accuracy and resolution of LiDAR data allow for more reliable modelling of surface water dynamics, supporting effective water resource management, flood risk assessment, and environmental planning.
LiDAR is a powerful tool for vegetation analysis because its laser pulses can penetrate vegetation canopies to reveal underlying ground surfaces. By subtracting vegetation heights from the data, analysts can create a “bare earth” model, which provides a clear view of the terrain beneath trees and other vegetation. This capability enables accurate assessment of forest canopy density, tree height and biomas. It also plays a critical role in evaluating wildfire risk, monitoring forest health and supporting sustainable land management practices.
Applications in Land Development
LiDAR data is highly valuable for site selection and grading in construction and development projects. Developers use the detailed elevation and terrain information to identify optimal locations for building, taking into account slope, drainage, and potential hazards. Accurate LiDAR-derived data also supports precise grading plans, allowing engineers to minimise earthwork costs, reduce project risks and optimise site preparation. By providing a clear understanding of the topography, LiDAR helps ensure more efficient, cost-effective and environmentally responsible construction planning.
LiDAR plays a critical role in infrastructure planning by providing highly accurate terrain data for projects such as roads, railways and utility corridors. Engineers and planners use LiDAR-derived data for alignment studies, cut-and-fill calculations and slope stability analysis, ensuring designs are both safe and efficient. The precision and detail offered by LiDAR help optimize construction strategies, reduce costs, and minimize environmental impact, making it an essential tool for modern infrastructure development.
LiDAR is a valuable tool for environmental impact assessments, helping evaluate how development projects affect natural features and landscapes. By generating high-resolution terrain models before and after development, LiDAR allows analysts to accurately assess changes in topography, vegetation and hydrological patterns. This detailed information supports informed decision-making, enabling planners to mitigate environmental impacts, protect sensitive ecosystems and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Case Study: Urban Redevelopment
In a recent urban redevelopment project, LiDAR data played a pivotal role in transforming an abandoned industrial area into a thriving mixed-use development. The client’s original brief emphasised not only maximizing land use but also preserving historical features and minimizing environmental risks. High-resolution LiDAR scans provided critical historical context, revealing buried structures, contamination hotspots and subtle terrain variations that were not visible through traditional survey methods.
Using this data, a detailed Digital Elevation Model (DEM) was created, allowing planners and engineers to identify elevation changes, optimise grading and assess flood risk zones. These insights directly influenced building placement, foundation design and stormwater management strategies, ensuring that the new development was both safe and sustainable.
Throughout the project, LiDAR-guided decisions enabled the integration of historical preservation with modern urban amenities, while also minimising environmental impact. By leveraging accurate, high-resolution terrain and structural data, the project team was able to optimize land use, reduce construction risks and deliver a redevelopment that balanced functionality, safety and heritage preservation.
Conclusion
LiDAR data unlocks a wealth of information for terrain modelling, environmental analysis and land development. As technology advances, its applications will continue to grow and development further multi-use datasets.
Data Source
Our LiDAR and elevation datasets are obtained from trusted national datasets provided by Bluesky and the Environment Agency, ensuring the highest standards of accuracy and reliability in all analyses.
If you have any further questions or want to explore LiDAR applications in more detail, feel free to reach out or head to www.centremapslive.co.uk